Gynecomastia
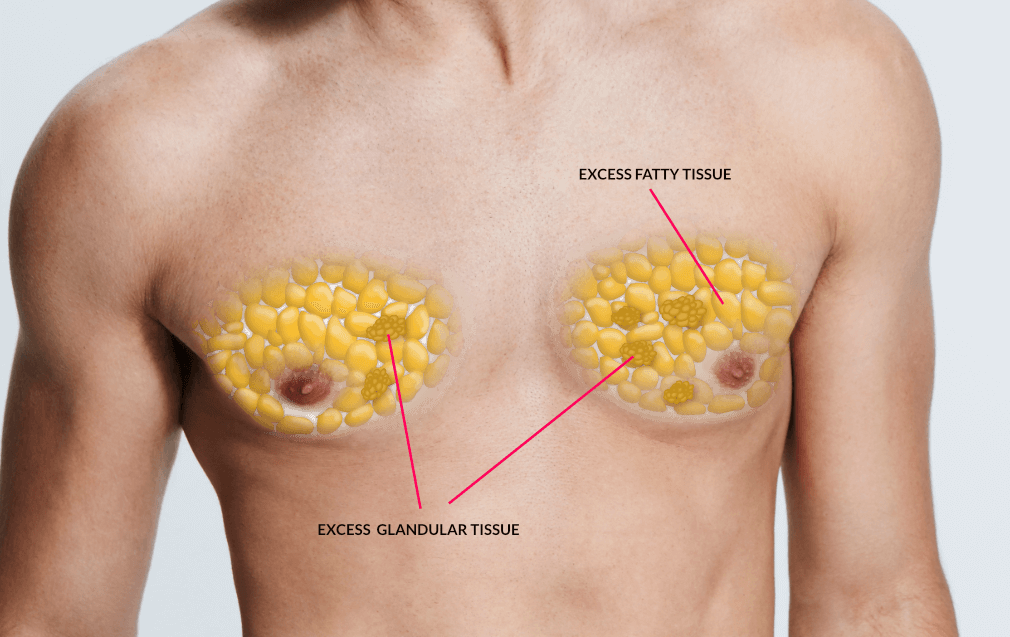
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of the glandular tissue in the male breast. This development is typically the result of an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones in the body. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly, and is common in infants, boys during puberty, and older men.
Various factors can contribute to developing gynecomastia, including natural hormone changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty or old age, can cause breast tissue to grow. Certain medications, such as anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some AIDS medications, can also cause gynecomastia. Health conditions that affect hormone levels, like hypogonadism, tumors, hyperthyroidism, and kidney failure, may also lead to this condition.
Gynecomastia Treatment Methods
Treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s discomfort or self-consciousness. If a medication or underlying health condition is causing gynecomastia, addressing that issue may resolve it.
Two primary procedures are used when surgery is required: liposuction and mastectomy. Liposuction involves the removal of breast fat but not the breast gland tissue itself, while mastectomy involves removing the breast gland tissue. The latter is often done endoscopically, requiring smaller incisions, and is typically less invasive than traditional surgery.

Gynecomastia surgery time, Anesthesia method, and Incisions
Gynecomastia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia but can also be done using local anesthesia with sedation, depending on the patient’s situation and the surgeon’s recommendation. The procedure usually takes about one to two hours, depending on the extent of the gynecomastia and the surgical method used.
Pre-Operative Preparation
Before gynecomastia surgery, patients should follow their surgeon’s specific instructions to ensure the best possible outcome. This may include guidelines on eating, drinking, and medication use. Patients should stop taking aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs, as they can increase bleeding. If the patient smokes, stopping before surgery is recommended, as smoking can impede the healing process.
Post-Operative Recovery Process
After gynecomastia surgery, patients must wear a compression garment for about two weeks to minimize swelling and support breast tissue healing. Swelling, bruising, and discomfort are common but can be managed with prescribed medications. Most patients return to non-strenuous work within a few days to a week. Physical activity, particularly lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercise, should be avoided for at least a few weeks.
As with any surgery, gynecomastia surgery leaves scars. However, these scars are usually along the edge of the areola and tend to fade significantly over time, becoming less noticeable.
At Unimed Health, we understand the emotional and physical distress that gynecomastia can cause. Our experienced team is here to guide you through every step of your journey, from consultation through recovery. We utilize state-of-the-art surgical techniques to ensure you achieve the most natural and satisfying results. Contact us today to schedule your consultation and take the first step on your path to a more confident you.
